
RTO THERMAL OXIDIZERS AND VOC CONCENTRATORS
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizers are one of the most preferred technologies for the reduction of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) pollutants and odors in process gases and exhaust gases.
Characteristics of RTO regenerative thermal oxidizers:- low energy consumption
- high efficiency of the energy process up to 98%
- the long service life of the device and the ceramic bed
- low maintenance and operating costs
- versatility and a wide range of applications
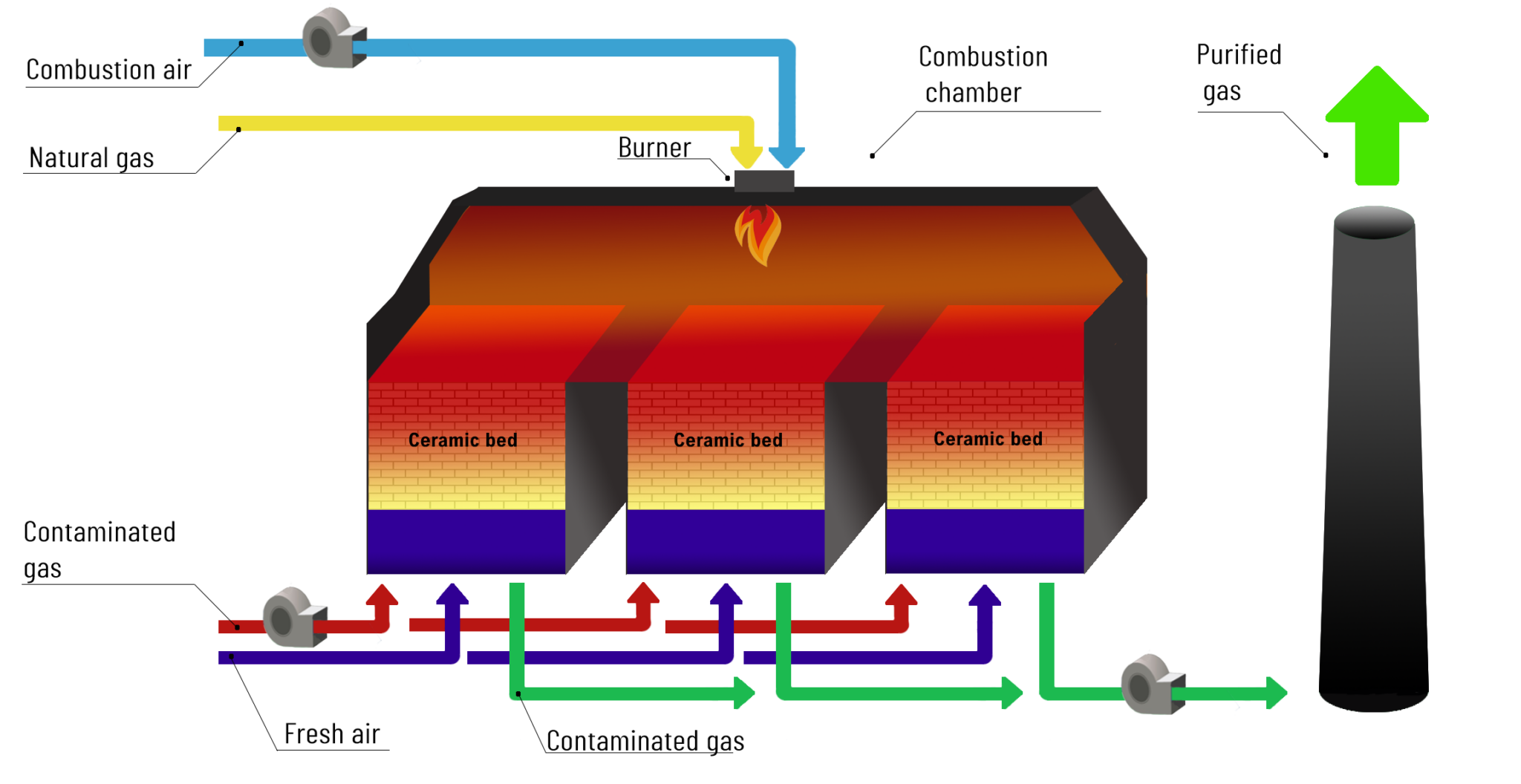
RTO regenerative thermal oxidizers are devices that, in the afterburning process, use the energy provided in neutralized gases, the energy generated in the process of burning volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and a small portion of the energy supplied to the process from the outside. The efficiency of the RTO oxidizers is high, therefore the demand for thermal energy is negligible, due to the high degree of recovery/regeneration of thermal energy inside the device and in the afterburning process through the use of a ceramic bed. The ceramic bed retains heat from the previous combustion cycle to heat and at the same time volatilizes the VOC compounds in the gases for the next cycle.
The RTO technology operates in a high-temperature range of 700-800ºC, which makes the oxidation of pollutants contained in gases one of the most effective, which allows meeting even strict standards of permissible emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere.
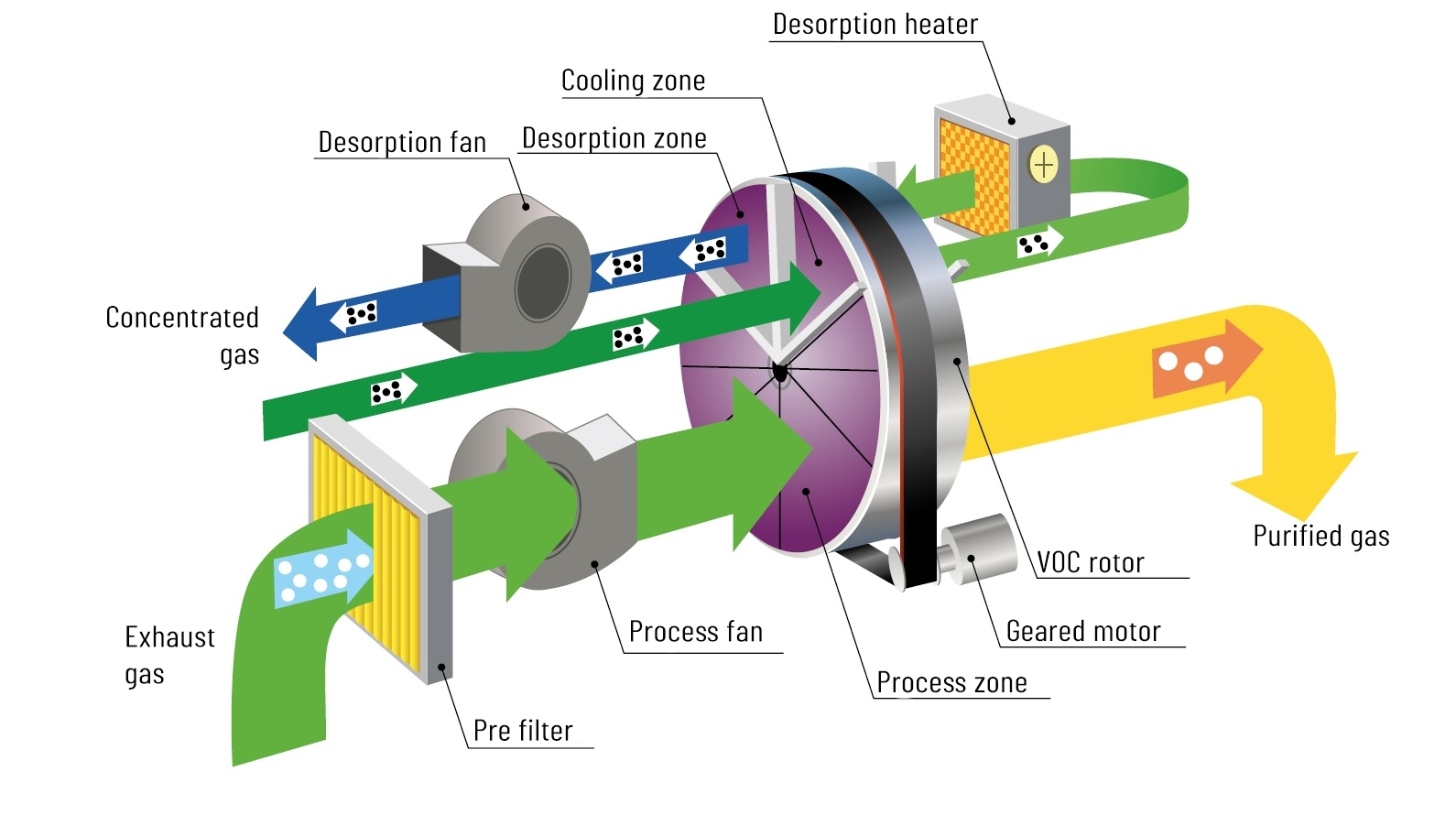
VOC concentrators are devices that use the adsorption process to trap VOCs, removing them from the process gas stream. VOC adsorption is carried out on specially prepared matrices, made of zeolites. Zeolites are porous aluminosilicates with a crystalline structure containing a system of channels and chambers to which they owe their unique properties and high specific surface area. Due to these features, they are very effective in capturing low VOC emissions and concentrating them into a much smaller stream of gases.
VOC concentrators are a solution that effectively increases any afterburning process, due to increasing the concentration of fuel in the afterburning process and reducing the ballast in the form of excess air.


© Copyright 2021 Vens Sp. z o.o.
Privacy Policy